India is the third largest automobile market in the world after the US and China but in electric vehicles, India is still miles away from being a hub. The EV market in India is becoming more diverse compared to other countries such as electric two wheelers, electric three wheelers, Electric cars and electric commercial vehicles.
Now, both the government and manufacturers are focusing on electric vehicles. According to the Economic Survey 2023, India’s electric vehicle market will grow at 49% CAGR (compound annual growth rate) by 2030 and this industry will create around 50 million direct and indirect jobs by 2030. The Government of India has introduced many policies and incentives to support the electric vehicle industry. The government plans to achieve a target of 30% in the sale of electric vehicles of the total vehicle fleet by 2030.
According to the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, 53,387 electric vehicles were registered in 2013 however 2,830,565 were registered till August 2023.
The Indian Government has launched many schemes for promoting electric vehicles and also to achieve net zero targets. Such as, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced Indian Rupee 35,000 crore capital investments to achieve net zero targets by 2070. The government launched FAME II (Faster Adoption of Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles Scheme) and PLI (Product Linked Incentive Scheme) for this budget and has allotted $ 631 million for this. The government announced to reduction of customs duty on imported lithium-ion and also exemptions of excise duty on the manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles. EVs play a major role in reducing air pollution. Indian Government commits to reducing its carbon footprint under the Paris Agreement.
Electric Vehicles Sales in India (Two Wheelers, Three Wheelers, Four Wheelers and Bus)
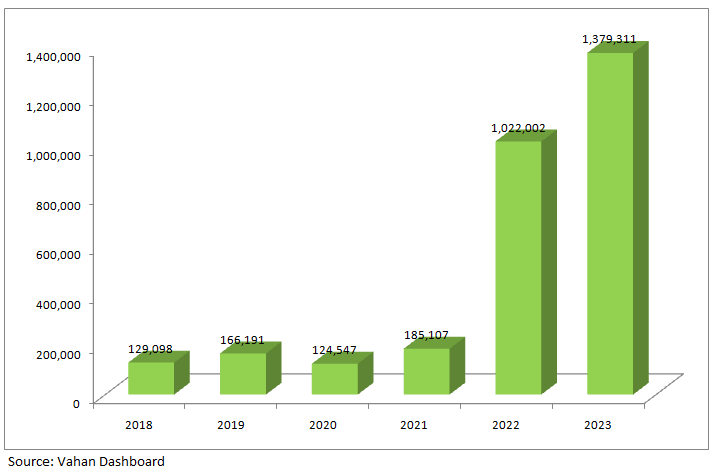
Electric Vehicles in India, Segment wise
Electric Two Wheeler: The electric two wheeler companies in India is rapidly increasing due to domestic demand, government policies and consumer awareness of the environment. The companies are offering a wide range of electric scooters and electric motorcycles. In India huge population of middle and lower middle class live in rural and urban areas and they mostly depend on two wheelers for their transportation. Electric two-wheeler is playing a significant role in the transportation landscape. The electric two wheeler market is very large and it is growing fastly in India.
Electric Two Wheeler Companies in India: Prominent electric two wheeler manufacturers in India are Ola Electric, Hero Electric, TVS Motors, Okinawa Autotech, Ampere Vehicles, Ather Energy, Kinetic Green and Bajaj Auto.
Electric Three Wheeler: Electric three wheeler transportation is very popular in India. It is also called battery rickshaws or e- rickshaws. This is the ideal mode of transportation for rural and urban areas because it is less expensive and requires less maintenance compared to gasoline three wheelers. The running cost of electric three wheeler is also very low when compared to other three wheeler. This vehicle is also available in CNG (Compress Natural Gas), LPG (liquefied Petroleum Gas), Petrol and Diesel. These three wheelers are perfect for urban areas and for narrow streets in rural areas. This vehicle is also serving as a means of shared transportation. These vehicles are providing a source of livelihood for many people.
Electric Three Wheeler Companies in India: India’s electric three wheeler manufacturers are Mahindra Electric, Piaggio Vehicles, Atul Auto, Lohia Auto and Kinetic Green.
Electric Cars: Many companies are contributing to the growth of the electric car market in India but electric cars are yet not very popular in India. Electric cars and their market are still developing. Electric cars face many challenges in India such as high price, limited companies and their limited models, battery technology, charging stations and consumer awareness. If all these issues are gradually resolved, then electric cars market will grow rapidly. Electric vehicles have fewer moving parts and require less maintenance compared to gasoline vehicles.
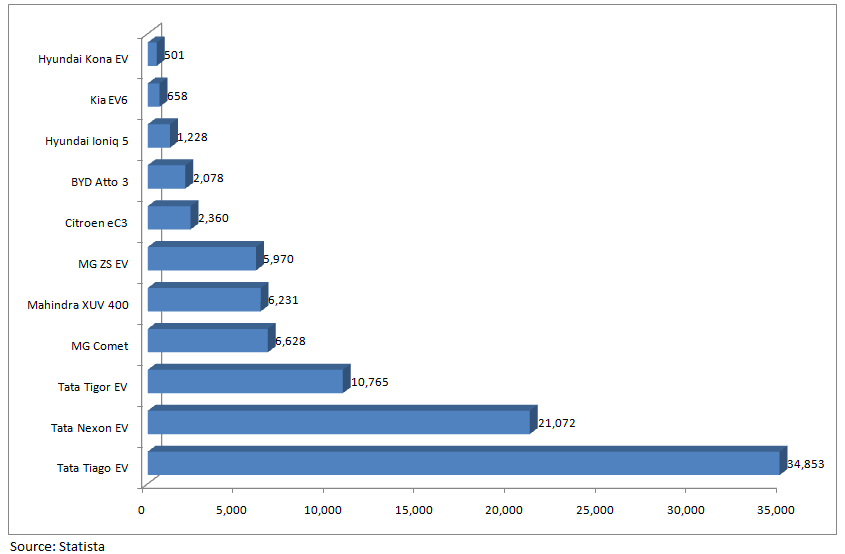
Electric Car Companies in India: Major players of electric car companies are Tata Motors, Mahindra & Mahindra, MG Motors, Swedish company Volvo, BYD, Kia and Hyundai. Tesla is also expected to enter the Indian electric car market this year.
Electric Cars Sales in India in 2024 by Model (Passenger Vehicle)
Electric Commercial Vehicles: The electric commercial vehicles market is still in its early stages in India. It is expected that it will take time to expand. Various state governments are running electric buses for public transportation. These electric buses are helping in reducing air pollution and dependency on fossil fuels.
Government Support and Policies: The adoption of EVs will not only boost the Indian economy but it will also help in achieving net zero emissions by 2070.
FAME Scheme: It is part of the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan. FAME Phase I (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) was launched in 2015 and completed in 2019 in India. FAME Phase II was launched in 2019. The objective of this scheme was to encourage the adoption of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles and reduce dependency on fossil fuel.
- PLI Scheme: Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme was launched for the automotive sector in Sept 2021 to increase manufacturing in the automotive sector.
- PLI Scheme National Program on Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage: This scheme was launched in 2021 to increase the manufacturing capabilities of electric mobility and battery storage.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) has been reduced from 18% to 5% on electric vehicles.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) has been reduced from 18% to 5% on chargers and charging stations.
- Waiver on road tax on the purchase of electric vehicles.
- Direct discount on the purchase of electric vehicles and tax benefits in income tax.
Challenges of Electric Vehicles in India: Indian electric vehicles face some challenges such as consumer awareness, high price, charging infrastructure, investment, innovation and collaboration between the government and the private sector but these challenges also give opportunities to overcome barriers.
- Consumer Awareness: Mostly consumers of India aren’t aware of the benefits of electric cars such as less operating cost compared to petrol or diesel cars, reduced carbon emission and subsidies given by the government on new electric car purchases. Electric vehicles improve air quality and public health. EVs can also reduce noise pollution.
- High Price: The price of electric cars is very high compared to internal combustion engine cars.
- Charging Infrastructure: The lack of charging stations is also a big barrier to electric car growth. The Indian government needs to create a charging network across the nation.
Future of Electric Vehicles in India: The Government should continue investments in infrastructure for electric vehicles. Enhance the technology and market through collaborations with international manufacturers. This will boost the growth of the electric vehicle market in India and in this way, India will rapidly adopt EVs in all segments in the near future.
CONCLUSION
India is the third largest automobile market in the world but in electric vehicles, India is still miles away from being a hub. India imports huge amounts of crude oil and spends a lot on it. The adoption of EVs will not only boost the Indian economy but it will also help in achieving net zero emissions by 2070. So the government has launched many schemes for promoting electric vehicles. In the near future, India will rule the world as a hub of EVs.

